What Is Building Information Modeling (BIM)?
Building Information Modeling (BIM) is a digital process that creates a 3D model of a construction project. It includes physical and functional characteristics. Unlike traditional blueprints, BIM provides a dynamic, data-rich model that improves planning, execution, and maintenance.
Why Is BIM Essential in Today’s Construction Industry?
BIM allows better decision-making. It enhances coordination between stakeholders, architects, and engineers. The digital model helps identify conflicts early. That reduces costly rework during construction. BIM also offers real-time collaboration, ensuring all teams stay aligned.
Key Benefits of Using BIM

Improved Accuracy and Visualization
BIM allows users to see the building from every angle. This makes it easier to spot issues. Accurate models lead to better design and fewer surprises during construction.
Faster Project Completion
Teams can share real-time updates. This reduces delays and keeps everyone on schedule. Coordination among subcontractors becomes much easier.
Cost-Effective Planning
BIM helps forecast material quantities. This avoids over-purchasing and waste. Budget estimation is more precise, keeping the project within limits.
Risk Mitigation and Safety
By simulating different scenarios, BIM improves site safety. Hazards are identified early. Risk management becomes proactive instead of reactive.
How BIM Improves Collaboration Across Disciplines
BIM unifies the design, engineering, and construction workflows. All stakeholders can access a centralized model. Changes made by one team are visible to others instantly. That avoids duplication of efforts and keeps the project data consistent.
The Lifecycle of a BIM Project
1. Design Stage
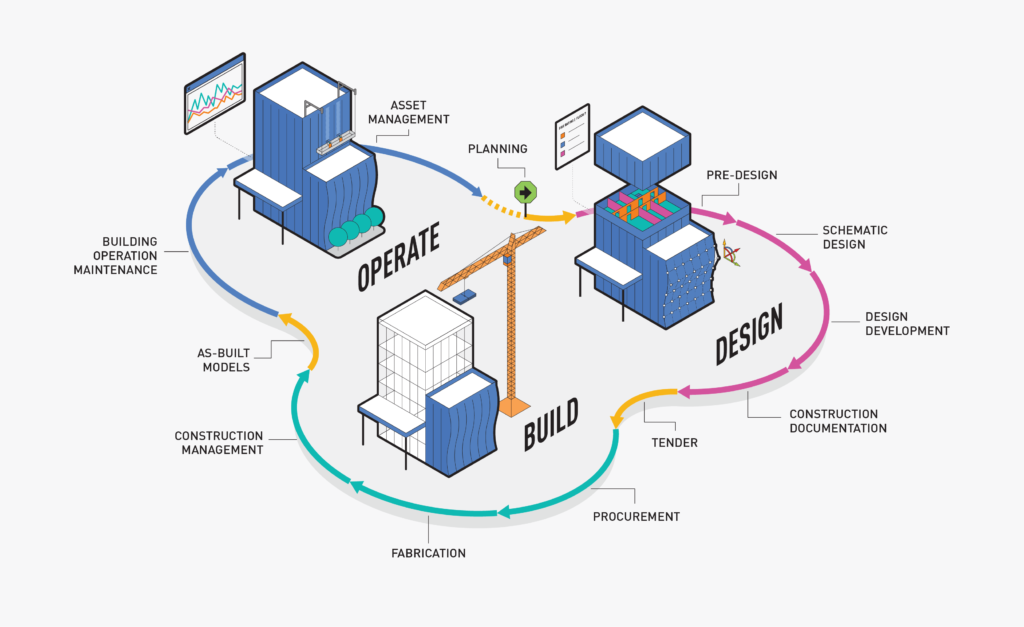
During this phase, architects and engineers collaborate. They use BIM software to develop models. These models include geometry, systems, and spatial relationships.
2. Construction Planning
Contractors analyze the model for logistics. They plan material deliveries, crew schedules, and sequencing. This reduces downtime.
3. Actual Construction
BIM ensures that on-site teams follow the approved model. Any changes in the field are updated in real time.
4. Operations and Maintenance
After handover, building managers use BIM for facility operations. It assists in managing repairs, energy use, and equipment tracking.
Most Popular BIM Software Solutions
- Autodesk Revit
- Navisworks
- Bentley Systems
- Trimble Tekla
- Graphisoft ArchiCAD
These tools help in modeling, clash detection, and construction simulation.
Challenges of BIM Adoption
While BIM is powerful, it has barriers. Some firms struggle with:
- High initial investment
- Training costs
- Resistance to change
- Interoperability between platforms
Still, the long-term ROI outweighs the challenges for most.
FAQs About Building Information Modeling
Q1: Is BIM only for large projects?
No. BIM benefits both large and small projects by improving accuracy and reducing costs.
Q2: Do all stakeholders need BIM training?
Yes. Each team member should understand BIM basics to collaborate effectively.
Q3: Can BIM be used after construction?
Absolutely. BIM supports maintenance, renovation, and future upgrades.
Q4: How is BIM different from CAD?
CAD focuses on 2D drafting. BIM is data-driven and 3D-based, offering much more detail and integration.
Q5: Is BIM mandatory by law?
In some countries, yes. Governments are increasingly requiring BIM for public infrastructure.
Conclusion: BIM Is the Future of Smart Construction
BIM transforms how we design, build, and manage spaces. It minimizes waste, improves safety, and cuts costs. More than a tool, it’s a new standard for modern construction. Teams that embrace BIM early gain a competitive edge and deliver better results.


